Itai-itai Disease
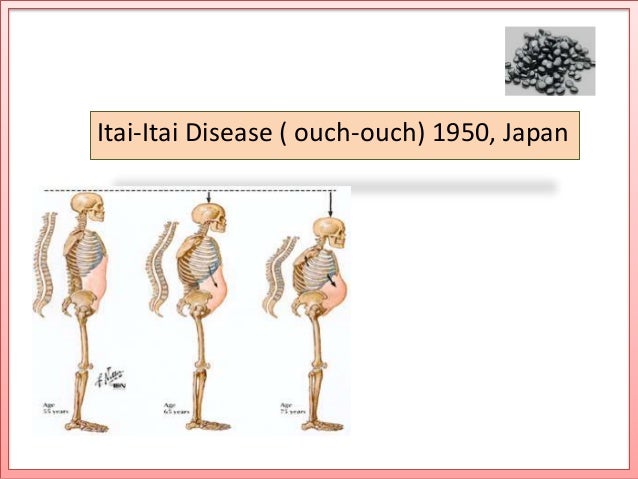
Itai-itai disease. O termo Itaí-itai traduzido do japonês para o português significa dói-dói ou também ai-ai e se deve à principal queixa do paciente. 1 2 Itai-itai disease is characterised by osteomalaecia with severe bone. Itai-itai disease is caused by cadmium Cd exposure produced as a result of human activities related to industrialisation and this condition was first recognised in Japan in the 1960s.
Patients experienced bone deformation severe pain related to bone effects and shortened lifespan. Dor causada por fraturas inexplicáveis dos ossos. Farlex Partner Medical Dictionary.
Die Itai-Itai-Krankheit ist eine in bestimmten Gegenden Japans endemisch vorkommende Erkrankung des Knochenapparates. Consequently the soil in rice paddies became polluted with heavy metals including cadmium through irrigation water streams from around 1910 to the 1960s. Itai-itai disease is the most severe form of chronic Cd poisoning caused by prolonged oral Cd ingestion.
Article in Japanese Hiramatsu H Hisada K Takashima T. A form of cadmium poisoning described in some Japanese people characterized by renal tubular dysfunction osteomalacia pseudofractures and anemia caused by ingestion of contaminated shellfish or other sources containing cadmium. 4923355 PubMed - indexed for MEDLINE Publication Types.
With chronic exposure people began developing itai-itai disease which is characterized by kidney disorders osteomalacia and osteoporosis. Die Itai-Itai-Krankheit ist eine seit den 50er Jahren auftretende Erkrankung die sich ausschließlich bei multiparen Frauen postmenopausal manifestiert. With itai-itai disease kidney function worsens for a long period of time due to cadmium poisoning resulting in fragile bones due to a lack of calcium.
Combined effects of estrogen deficiency and cadmium exposure on calcified hard tissues. Doença de itai-itai ou doença dói-dói é a denominação dada ao envenenamento de centenas de pessoas por cádmio ocorrido no Japão junto ao Rio Jintsu. Animal model relating to itai-itai disease in postmenopausal women.
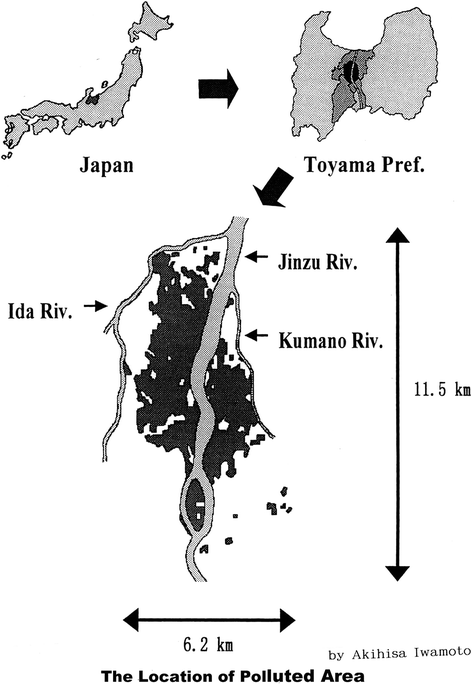
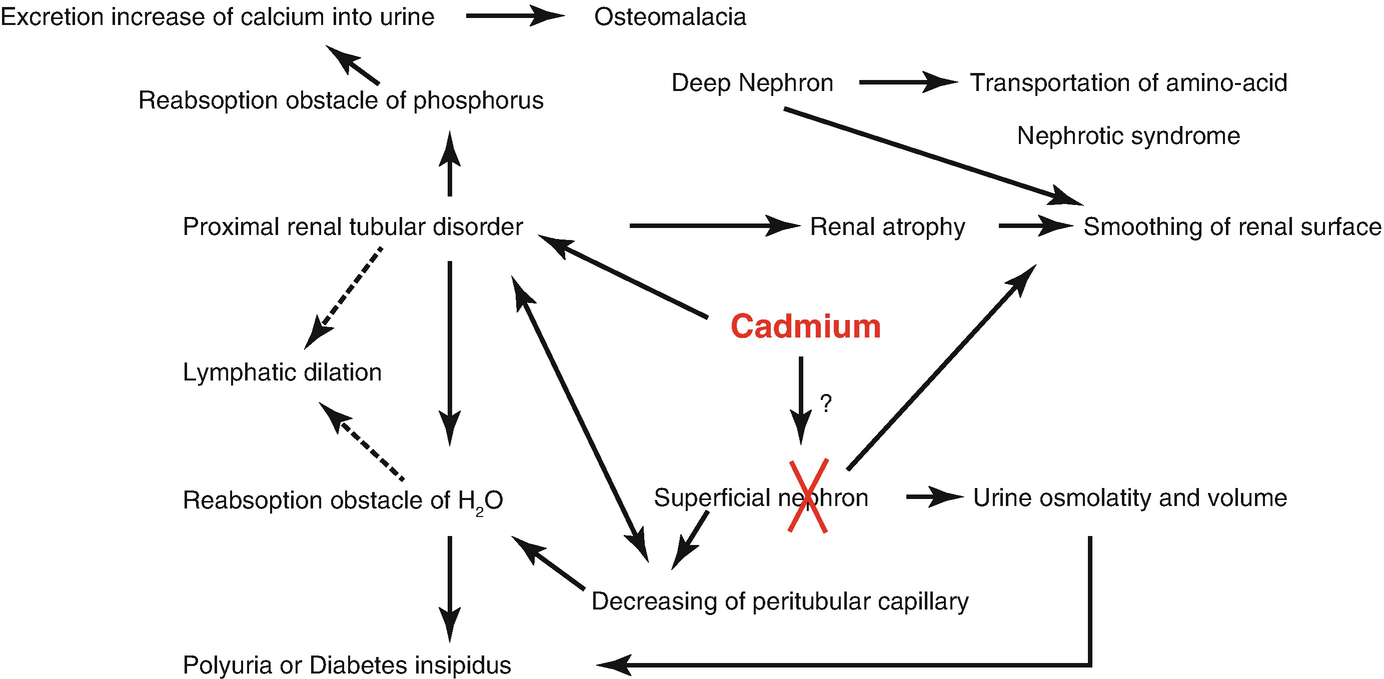
Itai-itai disease is considered to be a type of acquired Fanconi Syndrome characterized by renal tubular dysfunction and osteomalacia and has been found among middle aged and elderly women with relatively frequent pregnancy living in the cadmium polluted area for more than 30 years. It developed in numerous inhabitants of the Jinzu River basin in.
Itai-itai disease is considered to be a type of acquired Fanconi Syndrome characterized by renal tubular dysfunction and osteomalacia and has been found among middle aged and elderly women with relatively frequent pregnancy living in the cadmium polluted area for more than 30 years.
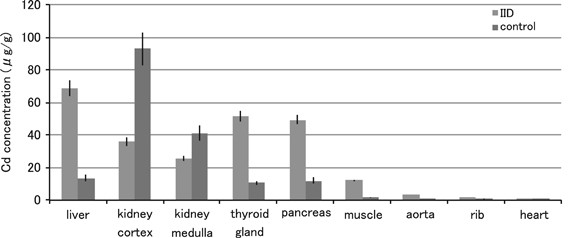
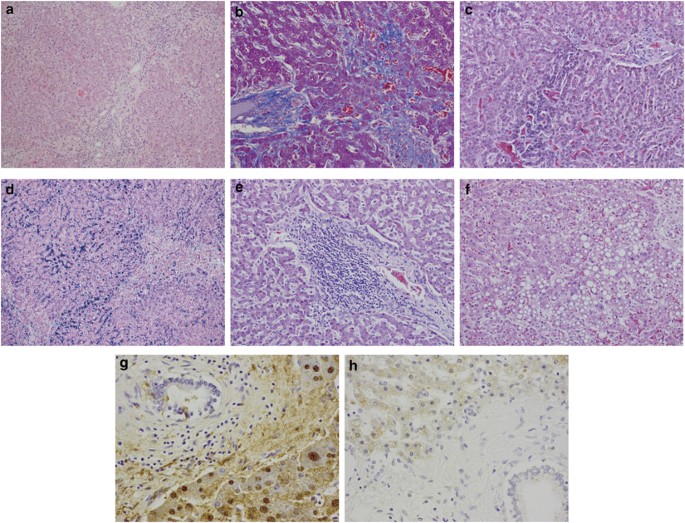
Itai-itai disease is considered to be a type of acquired Fanconi Syndrome characterized by renal tubular dysfunction and osteomalacia and has been found among middle aged and elderly women with relatively frequent pregnancy living in the cadmium polluted area for more than 30 years. In this area the river was contaminated by slags from a mine upstream. Itai-itai ouch-ouch disease caused by cadmium Cd exposure is considered a type of osteomalacia and is characterized by increased osteoid formation with low-grade bone mineralization. Itai-itai disease is considered to be a type of acquired Fanconi Syndrome characterized by renal tubular dysfunction and osteomalacia and has been found among middle aged and elderly women with relatively frequent pregnancy living in the cadmium polluted area for more than 30 years. With chronic exposure people began developing itai-itai disease which is characterized by kidney disorders osteomalacia and osteoporosis. Itai-itai disease is a type of acquired Fanconi syndrome characterised by renal tubular dysfunction and osteomalaecia induced by chronic Cd exposure through contaminated rice and drinking water2 3 6 Patients with Itai-itai disease demonstrate a Cd body burden indicated by Cd concentrations in the liver that is remarkably higher geometrical mean of 685 µgg wet weight than subjects in non. Itai-itai disease was officially recognized in 1968 as the first disease induced by environmental pollution in Japan after legal proceedings. The outbreak of itai-itai disease which is the most severe stage of chronic cadmium poisoning has occurred in the cadmium-polluted Jinzu River basin in Toyama. Die Itai-Itai-Krankheit ist eine in bestimmten Gegenden Japans endemisch vorkommende Erkrankung des Knochenapparates.
Itai-itai disease is caused by cadmium Cd exposure produced as a result of human activities related to industrialisation and this condition was first recognised in Japan in the 1960s. O termo Itaí-itai traduzido do japonês para o português significa dói-dói ou também ai-ai e se deve à principal queixa do paciente. Itai-itai disease was officially recognized in 1968 as the first disease induced by environmental pollution in Japan after legal proceedings. 1 2 Itai-itai disease is characterised by osteomalaecia with severe bone. In the early 1950s the local Dr Noburu Hagino tought that downstream of the Jinzu river the itai-itai disease a form of bone brittleness osteomalacia came from malnutrition but in 1957 the fact that the outbreak was concentrated in a limited area along the Jinzu River basin lead him to announce his explanation that the itai-itai disease was chronic cadmium poisoning caused by heavy metals. It developed in numerous inhabitants of the Jinzu River basin in. The basis of the court decision is simply but clearly shown in The view of the Ministry of Health and Welfare which consisted of 7 articles and was announced on 8th May 1968.




























Post a Comment for "Itai-itai Disease"