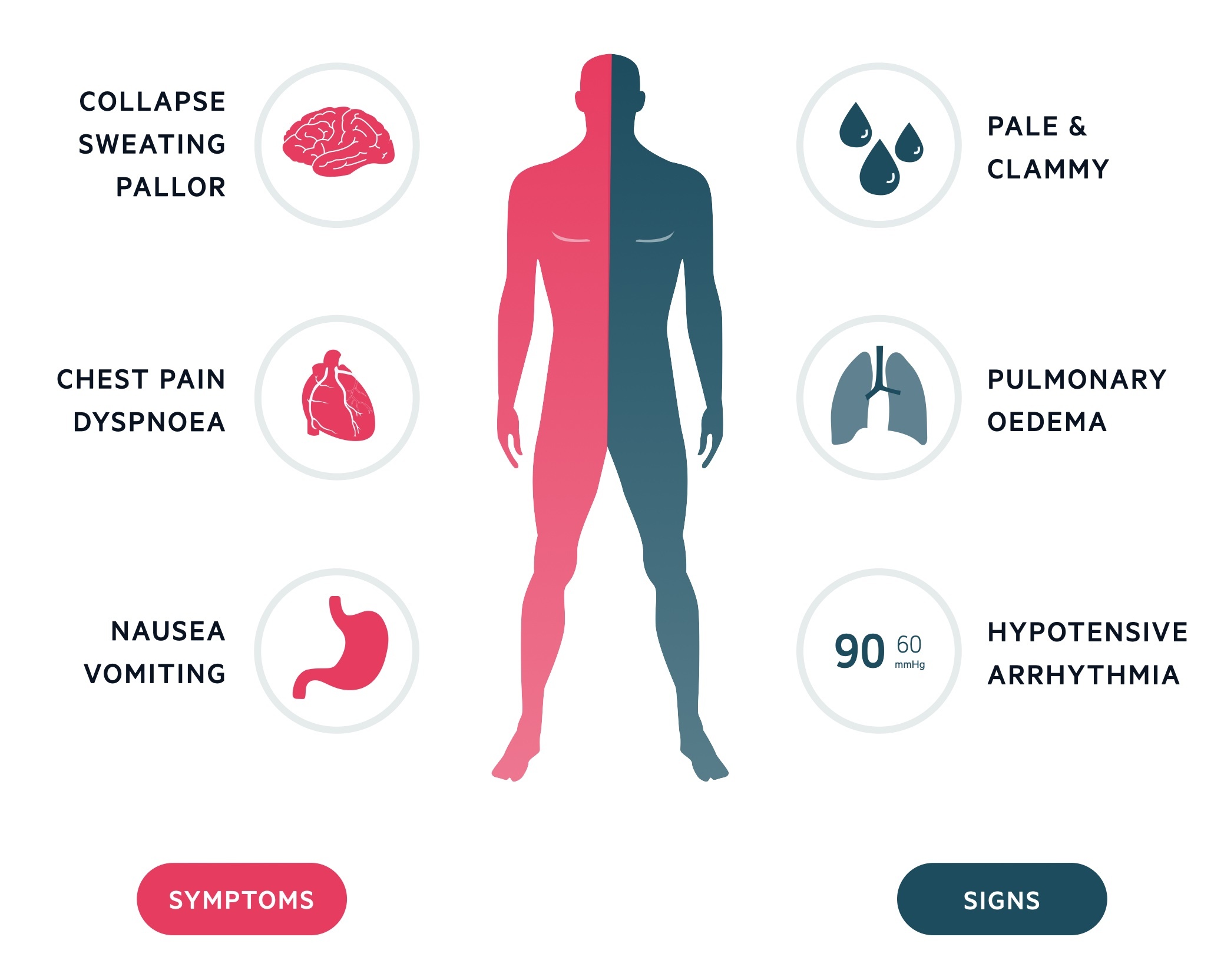
Acute Coronary Syndrome Presentation
Acute coronary syndrome presentation. Symptoms include shortness of breath dyspnea rapid breathing tachypnea and bluish skin coloration cyanosis. The journal serves the interest of both clinicians and researchers. The definition of ACS depends on the specific characteristics of each element of the triad of clinical presentation electrocardiographic changes and biochemical cardiac markers.
Acute coronary syndrome ACS is a medical emergency and requires immediate hospital admission. Acute coronary syndromes or heart attacks include unstable angina and acute myocardial infarction. Causes may include sepsis pancreatitis trauma pneumonia and aspiration.
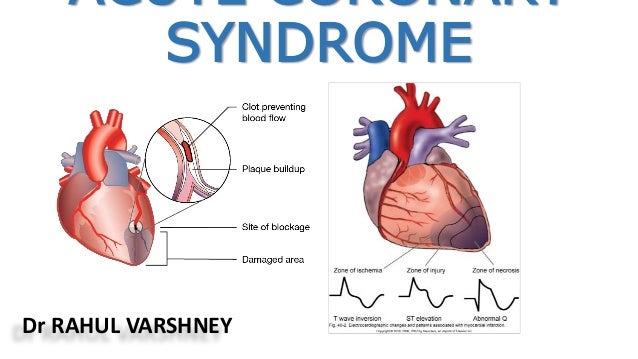
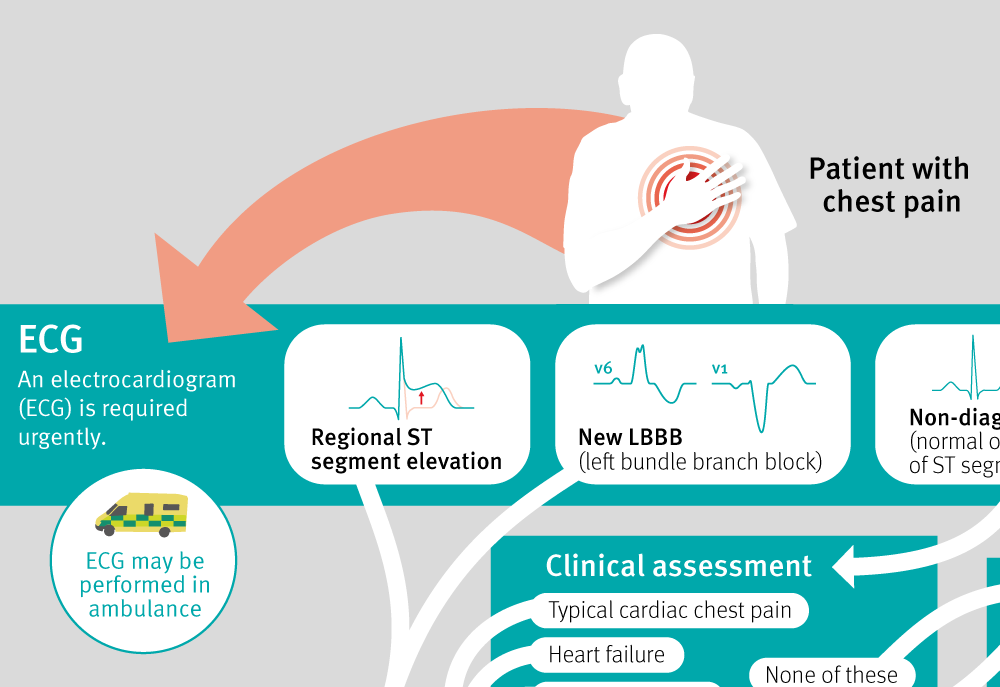
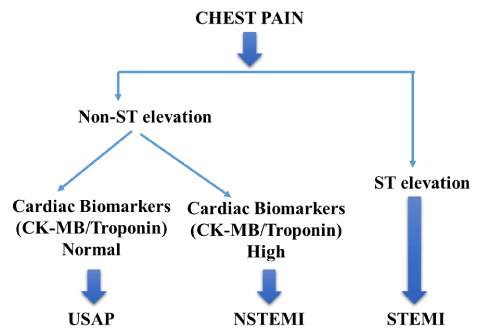
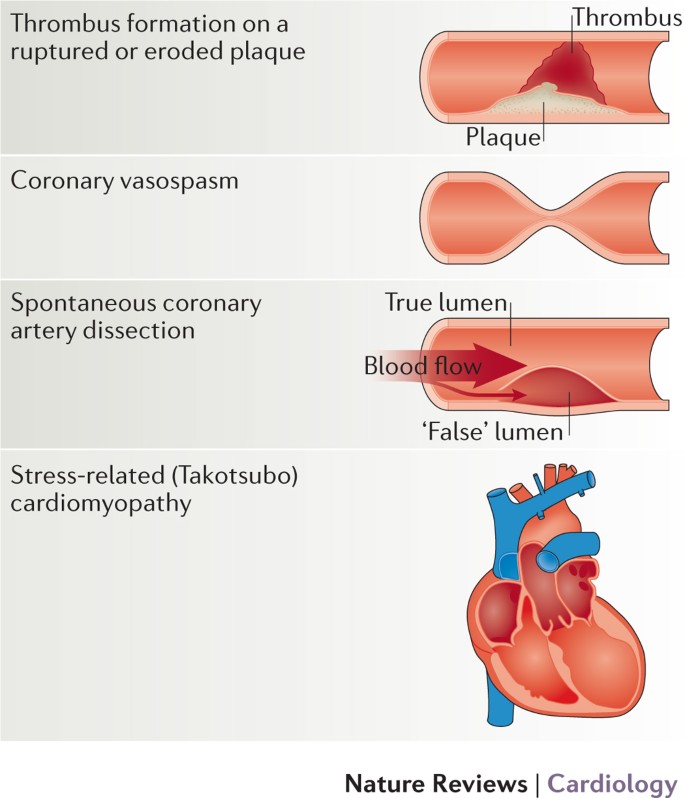
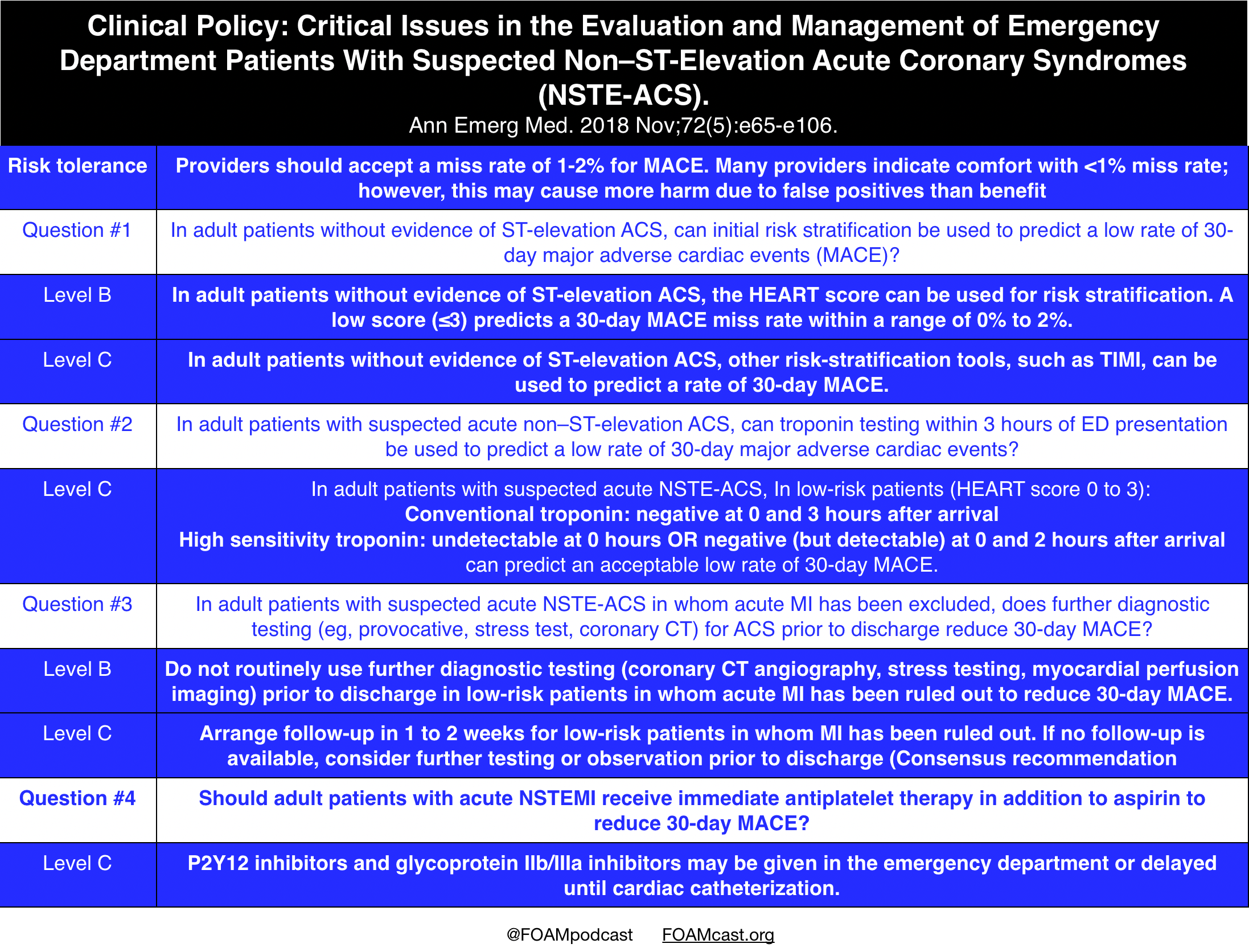
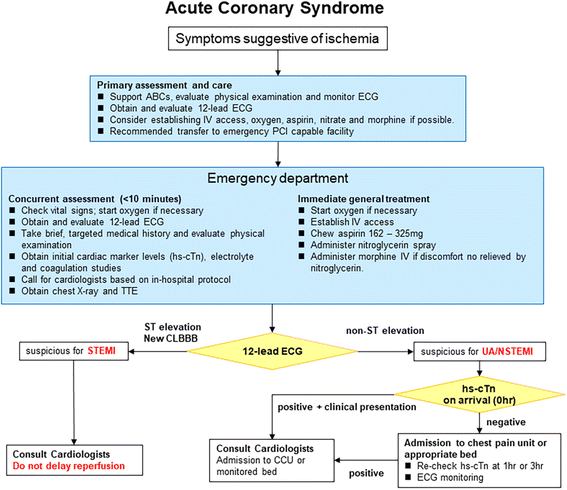
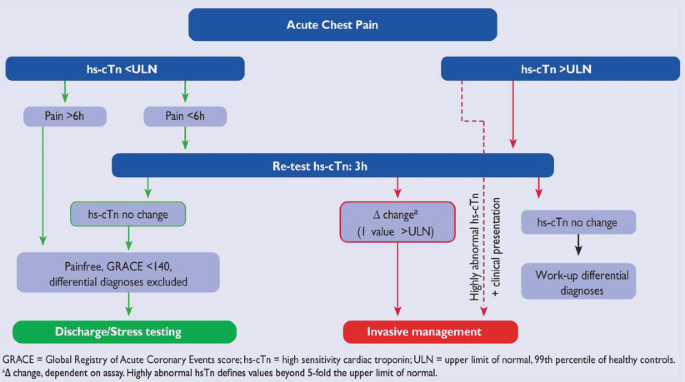
ACS is now classified mainly on the findings on the admission ECG and the results of serial cardiac troponin levels ACS refers to a range of acute myocardial ischaemic states which include. The latter is further classified according to electrocardiographic changes as non-ST elevation myocardial infarction NSTEMI and ST elevation myocardial infarction STEMI which comprise 61 and 39 respectively of admissions for acute myocardial infarction recorded in the. It is almost always associated with rupture of an atherosclerotic plaque and partial or.
It ranges from cardiac arrest electrical or haemodynamic instability with cardiogenic shock CS due to ongoing ischaemia or mechanical complications such as severe mitral regurgitation to patients who are already pain free again at the time of presentation. The primary outcome net adverse clinical events death MI stent thrombosis stroke target vessel revascularization or Thrombolysis in Myocardial Infarction TIMI major bleeding at 12 months occurred in 39 of the ticagrelor monotherapy after 3 months of DAPT group compared with 59 of the standard therapy group p 001. ViewPrint Table STRENGTH OF.
Acute coronary syndrome ACS refers to a spectrum of acute myocardial ischaemia andor infarction. Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction NSTEMI ST-elevation MI STEMI and unstable angina are the three traditional types of ACS. Understanding the diagnostic approaches as well as pharmacological and coronary interventions is crucial given the prevalence of ACS.
In addition to original papers we are launching a range of new manuscript types including Consensus and Position Papers Systematic Reviews Meta-analyses and Short communications. The International Journal of Cardiology is devoted to cardiology in the broadest sense. One such condition is a heart attack myocardial infarction when cell death results in damaged or destroyed heart tissue.
The clinical presentation of acute coronary syndromes ACS is broad. ACS may occur in the absence.
Acute coronary syndrome ACS refers to a spectrum of acute myocardial ischaemia andor infarction.
Both basic research and clinical papers can be submitted. Non-ST-elevation myocardial infarction NSTEMI ST-elevation MI STEMI and unstable angina are the three traditional types of ACS. Patients present with acute chest pain and persistent 20 minutes. Acute coronary syndrome ACS refers to a spectrum of clinical presentations ranging from those for ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction STEMI to presentations found in nonST-segment elevation myocardial infarction NSTEMI or in unstable angina. The purpose of this scientific statement is to propose and support a radial-first strategy in the United States for patients with acute coronary syndromes. Management of these are similar with important distinctions depending on the category of acute coronary syndrome. Acute coronary syndrome ACS refers to a spectrum of acute myocardial ischaemia andor infarction. The International Journal of Cardiology is devoted to cardiology in the broadest sense. ViewPrint Table STRENGTH OF.
A growing body of evidence supports adoption of transradial artery access to improve acute coronary syndromerelated outcomes to improve healthcare quality and to reduce cost. Symptoms include shortness of breath dyspnea rapid breathing tachypnea and bluish skin coloration cyanosis. The latter is further classified according to electrocardiographic changes as non-ST elevation myocardial infarction NSTEMI and ST elevation myocardial infarction STEMI which comprise 61 and 39 respectively of admissions for acute myocardial infarction recorded in the. A growing body of evidence supports adoption of transradial artery access to improve acute coronary syndromerelated outcomes to improve healthcare quality and to reduce cost. Acute coronary syndrome ACS is a medical emergency and requires immediate hospital admission. In 2009 approximately 683 000 patients were discharged from US hospitals with a diagnosis of acute coronary syndrome ACS. Thygesen K Alpert JS Jaffe AS et al.



















60212-6.fp.png)










33665-3.fp.png)

Post a Comment for "Acute Coronary Syndrome Presentation"