Management Of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome
Management of meconium aspiration syndrome. A policy of minimal handling should be applied to all babies with severe hypoxaemic respiratory failure since agitation can itself worsen gas exchange. The meconium stool then mixes with the amniotic fluid that surrounds the fetus. The concepts of pathophysiology and management of meconium stained amniotic fluid MSAF and meconium aspiration syndrome have undergone tremendous change in recent years.
Signs of meconium aspiration syndrome include tachypnea nasal flaring retractions cyanosis or desaturation rales rhonchi and greenish yellow staining of the umbilical cord nail beds or skin. If there is sign of fetal distress correctivemeasure should be undertaken or infantshould be delivered in timely manner. Meconium aspiration syndrome MAS mainly affects term or post-term infants and can be defined as the.
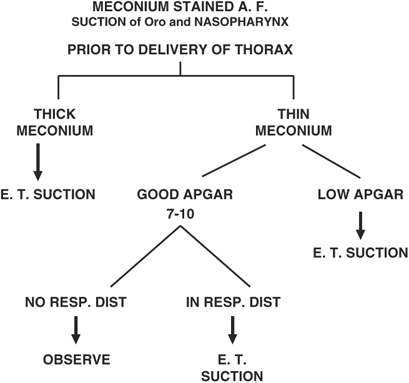
When there is meconium stained liquor careful suctioning of posterior pharynx after delivery of head decreases the potential for aspiration of meconium. In a tertiary care paediatric intensive care unit 17 term neonates with severe MAS were managed with HFOV used as the initial mode of ventilation and prospectively evaluated. Management Prenatal management.
Meconium aspiration syndrome MAS is a common respiratory disorder in term and near-term neonates. Broad-spectrum antibiotics used include ampicillin and gentamicin. Identification of high risk pregnancies andclose monitoring.
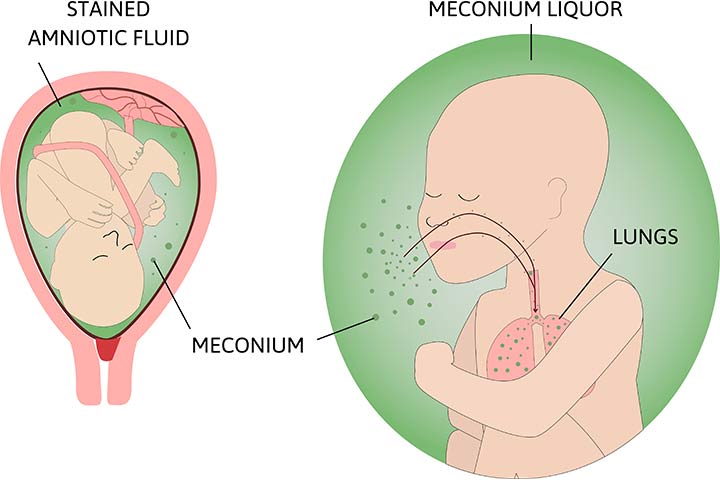
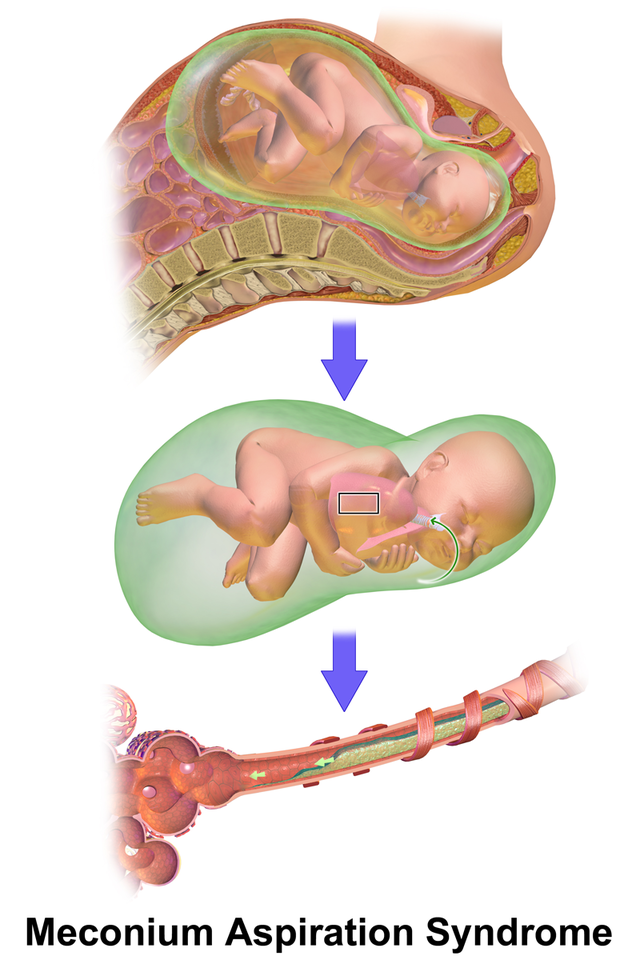
It occurs exclusively in the immediate neonatal period. Meconium staining may be visible in the oropharynx and on intubation in the larynx and trachea. Your baby may then breathe the meconium and amniotic fluid mixture into their lungs shortly before during or.
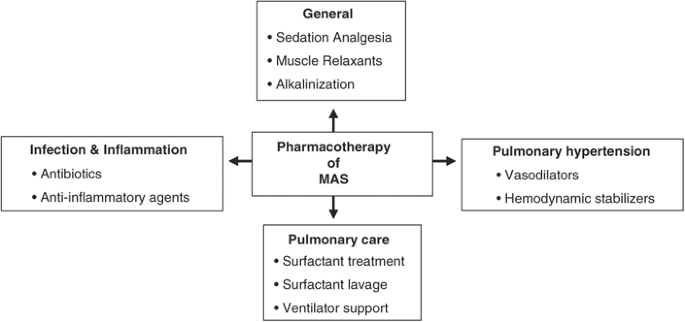
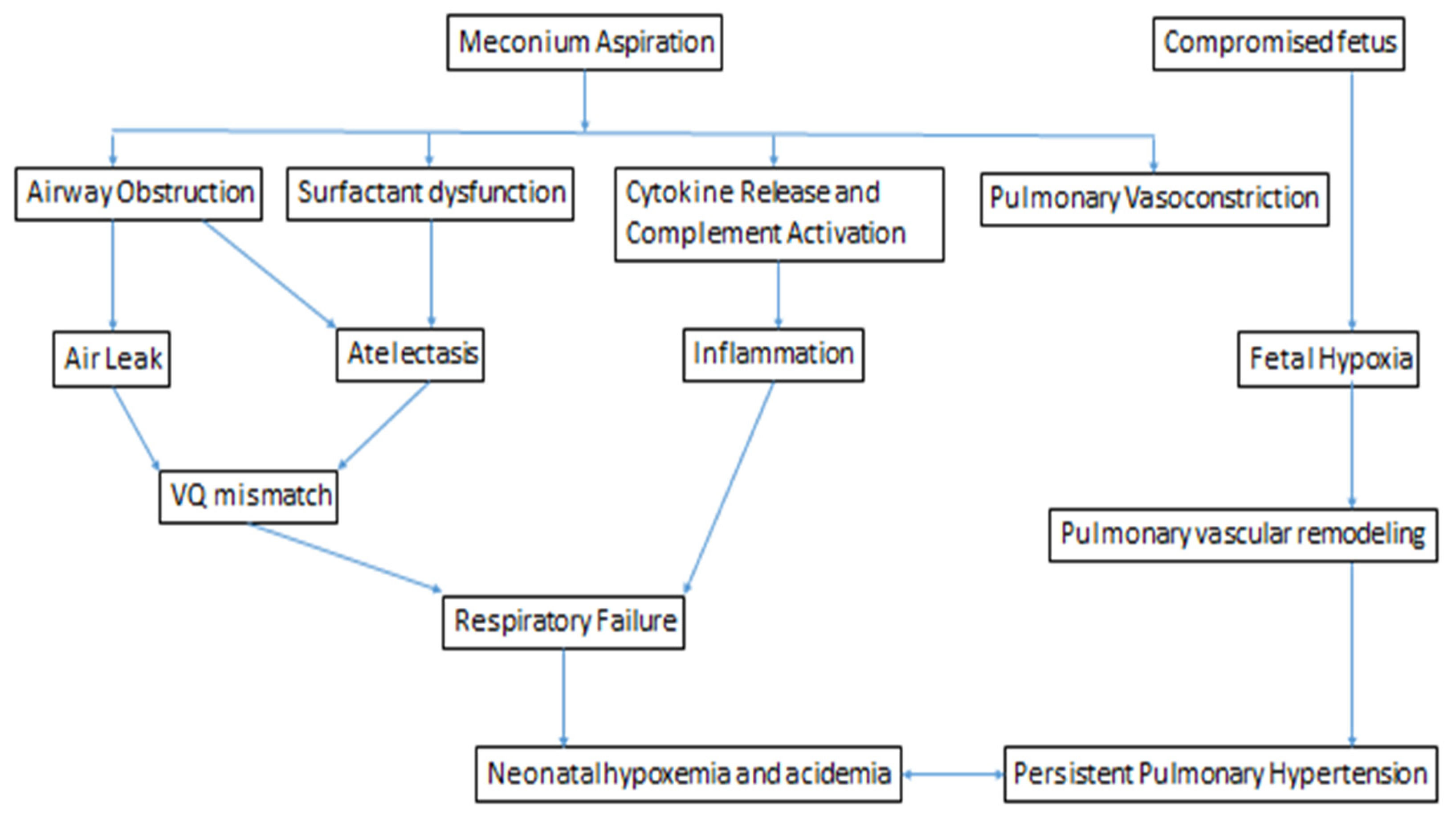
Thus the current strategies of management of MAS are the selective intubation with toileting only on infants with severe distress at birth and the early airway lavage with diluted surfactant solution followed by high frequency oscillatory ventilation which may prevent the further injuries in. In this paper the management of this syndrome is. 1 Despite rapid advances in diagnostic and therapeutic modalities over the past decades meconium and its effects on fetus and neonates have remained a cause of significant worry for both the.
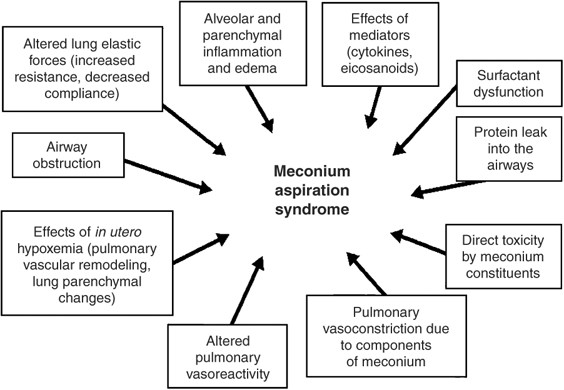
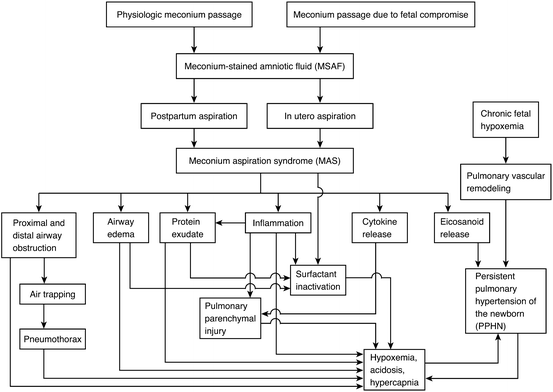
Meconium aspiration syndrome MAS is a result of ante- or postpartum aspiration of meconium-stained amniotic fluid in term or near-term infants resulting in respiratory morbidity of varying severity. 1 Rossi EM Philipson EH Williams TG et al.
Management of infants with meconium aspiration syndrome General supportive care.
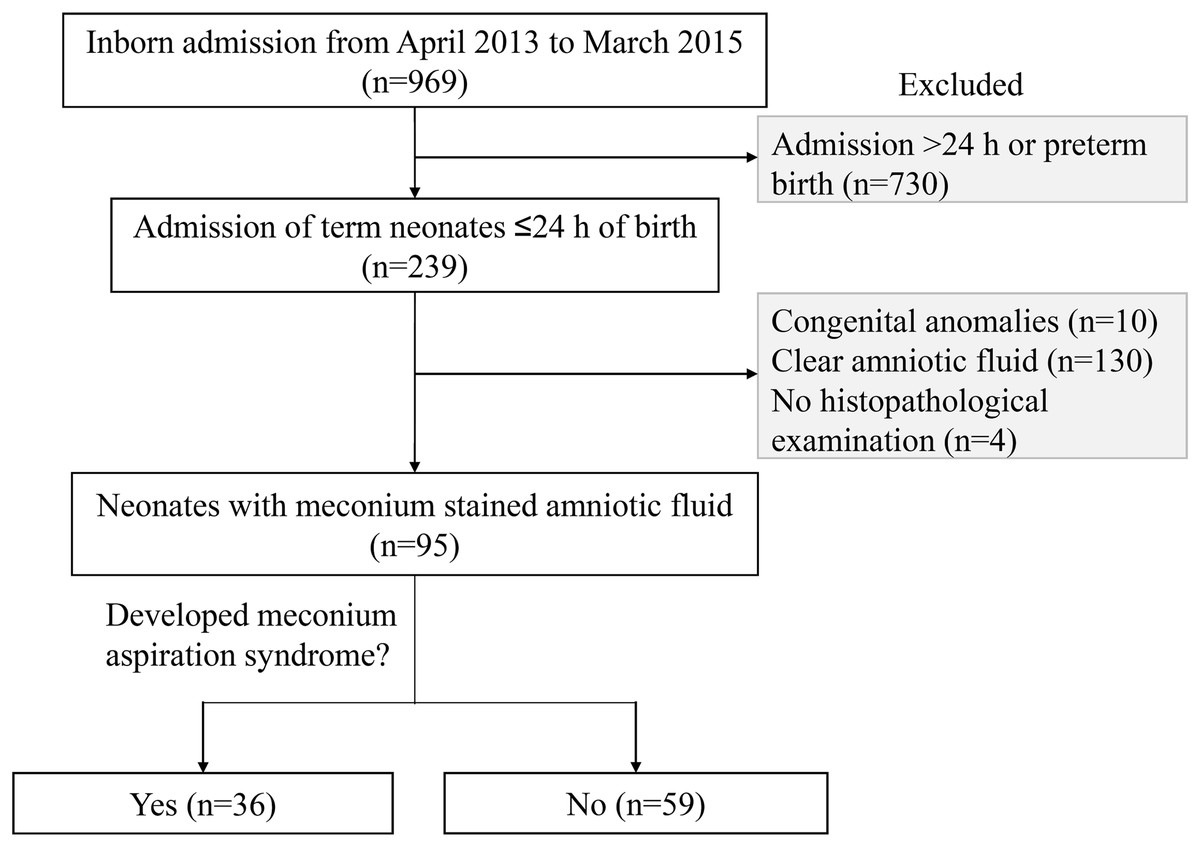
If meconium is passed more than 4 hours before delivery the infants skin will be meconium stained. Intrapartum and neonatal attributes. Your baby may then breathe the meconium and amniotic fluid mixture into their lungs shortly before during or. A policy of minimal handling should be applied to all babies with severe hypoxaemic respiratory failure since agitation can itself worsen gas exchange. Management Prenatal management. Pregnancy that continuepast due date induction as early as 41 weeksmay help prevent meconium aspiration. It occurs exclusively in the immediate neonatal period. Treatment with antibiotics should be discontinued if 48-hour blood cultures are negative and the infant is asymptomatic. To evaluate the effectiveness of HFOV used as the initial mode of ventilation in neonates with severe meconium aspiration syndrome MAS.
Most infants born through MSAF do not require resuscitation at. Release of meconium into the amniotic fluid is usually the result of in utero hypoxia andor fetal distress. Meconium aspiration syndrome MAS is a common respiratory disorder in term and near-term neonates. Pregnancy that continuepast due date induction as early as 41 weeksmay help prevent meconium aspiration. Meconium staining may be visible in the oropharynx and on intubation in the larynx and trachea. Management of infants with meconium aspiration syndrome General supportive care. Meconium aspiration syndrome MAS mainly affects term or post-term infants and can be defined as the.




































Post a Comment for "Management Of Meconium Aspiration Syndrome"